Featured
Table of Contents
Vpn Troubleshooting Guide - Freethought

The Routing and Remote Gain access to snap-in lives within the Microsoft Management Console, called the MMC. There are several ways to access the MMC. You can select the console from the Start menu's Programs choices, within the Administrative Tools folder within Windows server's Control board or by typing mmc at a command prompt.
As Tech, Republic's Brandon Vigliarolo demonstrates within his video at the start of this short article, the Providers console shows the status of the Routing and Remote Access entry. From within the Providers console and with the Routing and Remote Gain access to entry highlighted, you can click Start the Service or right-click the entry and choose Restart.
Often the VPN client and VPN server are set to using different authentication approaches. Validate whether an authentication mistake is the problem by opening the server console. Yet another technique of accessing the MMC is to type Control+R to open a command timely in which you can type mmc and hit Go into or click OK.
If the entry isn't present, click File, select Add/Remove Snap-in, select the Routing and Remote Gain access to alternative from the options and click Include, then OK. With the Routing and Remote Gain access to snap-in added, right-click on the VPN server and click Residences. Review the Security tab to validate the authentication approach.
7 Common Vpn Problems And How To Fix Them (Tested ...
Ensure the VPN customer is set to the authentication approach defined within the Security tab. Normally the products just examined are responsible for a lot of VPN connection rejection errors. However other basics should be correct, too. For instance, if the Windows Server hosting the VPN hasn't signed up with the Windows domain, the server will be not able to verify logins.
IP addresses are another basic component for which administration must be appropriately set. Each Web-based VPN connection usually utilizes two various IP addresses for the VPN client computer system. The first IP address is the one that was designated by the customer's ISP. This is the IP address that's utilized to establish the initial TCP/IP connection to the VPN server online.
This IP address usually possesses the exact same subnet as the local network and thus permits the customer to interact with the regional network. When you established the VPN server, you need to configure a DHCP server to appoint addresses to clients, or you can produce a bank of IP addresses to designate to customers straight from the VPN server.


If this option is selected and the efficient remote gain access to policy is set to enable remote gain access to, the user will have the ability to connect to the VPN. Although I have actually been not able to re-create the scenario personally, I have heard rumors that a bug exists in older Windows servers that can trigger the connection to be accepted even if the reliable remote gain access to policy is set to reject a user's connection.
Getting Started With Vpn Troubleshooting
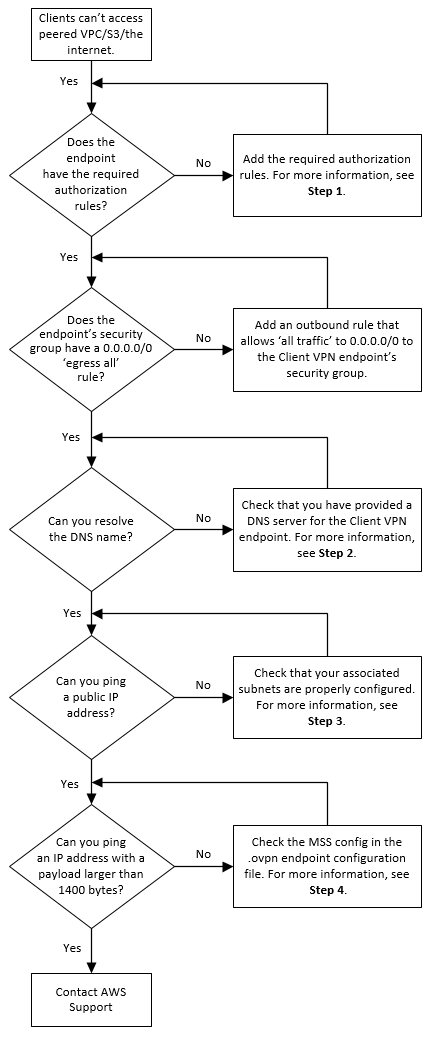
Another typical VPN problem is that a connection is successfully developed however the remote user is unable to access the network beyond the VPN server. By far, the most typical cause of this issue is that authorization hasn't been given for the user to access the entire network. To enable a user to access the whole network, go to the Routing and Remote Gain access to console and right-click on the VPN server that's having the problem.
At the top of the IP tab is an Enable IP Routing check box. If this check box is made it possible for, VPN users will be able to access the rest of the network, presuming network firewall programs and security-as-a-service settings allow. If the checkbox is not chosen, these users will be able to gain access to just the VPN server, but absolutely nothing beyond.
If a user is dialing straight into the VPN server, it's generally best to set up a fixed path between the client and the server. You can configure a fixed route by going to the Dial In tab of the user's residential or commercial properties sheet in Active Directory site Users and Computers and picking the Apply A Fixed Path check box.
Click the Include Route button and then go into the location IP address and network mask in the space offered. The metric should be left at 1. If you're using a DHCP server to designate IP addresses to customers, there are a couple of other problems that could trigger users not to be able to exceed the VPN server.
Troubleshooting - Barracuda Campus
If the DHCP server designates the user an IP address that is already in usage somewhere else on the network, Windows will spot the dispute and prevent the user from accessing the rest of the network. Another common problem is the user not receiving an address at all. Many of the time, if the DHCP server can't appoint the user an IP address, the connection won't make it this far.
254.x. x variety. If the client is assigned an address in a range that's not present within the system's routing tables, the user will be not able to navigate the network beyond the VPN server. Other problems can contribute to this issue, too. Make sure the resources the user is trying to gain access to are in fact on the network to which the user is connecting.
A VPN connection to the other subnet might, in fact, be required. A firewall program or security as a service solution might likewise be to blame, so don't forget to evaluate those options' settings, if such parts are present between the VPN server and the resources the user seeks to reach.
The very first possibility is that one or more of the routers involved is performing IP packet filtering. I recommend examining the customer, the server and any machines in between for IP packet filters.
Latest Posts
The 5 Best Business Vpn To Secure Your Team In 2023
The Best Free Vpn For Android
How To Troubleshoot Common Issues With Avg Secure Vpn